Q&A
Q: Do you really save electricity by switching to LED bulbs?
A: The luminous efficacy chart is as below: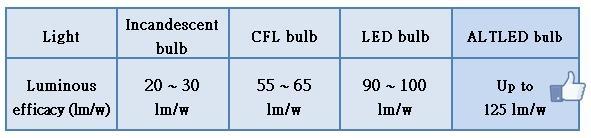
Q: Do LED T8 tubes really save you electricity?
A: Yes, it most definitely does. Although the energy saving percentage isn’t as high as compared with the incandescent bulb, LED lights will always be much more efficient than any traditional light source. Luminous efficacy of an ALTLED T8 tube reaches up to 130 lm/w.
Q: How can LED light bulbs replace traditional light bulbs? What are its advantages?
A: LED MR16, LED tubes, LED bulbs save more electricity, last a lot longer, need less maintenance, and are much more environmentally friendly.
Q: Where can you use LED MR16, LED Tubes and LED bulbs?
A:
● Commercial (restaurants, shopping malls, display centers, etc.)
● Public areas (streetlights, bus stops, parking lots, etc.)
● Schools (gymnasiums, libraries, laboratories, etc.)
● Hotels (lobbies, outdoor landscaping, etc.)
● Plants, residential, industrial and office lighting
Q: Do LED MR16, LED Tubes and LED bulbs heat-up after a long period of usage?
A: To stable the quality of LED lights is the ability to efficiently direct the heat away from the LED chips. One of ALT’s biggest advantages is, Glacier Edge™, the heat dissipation technology which has been patented and protected all over the world. The technology had been inherited from ALT_INC, the fourth largest server provider in the world, which is ALT’s associated business partner.
Q: How can LED light bulbs replace traditional light bulbs? What are its advantages?
A: LED MR16, LED tubes, LED bulbs save more electricity, last a lot longer, need less maintenance, and are much more environmentally friendly.
Q: Do grow lights really work for plants?
A: Yes. LED grow lights provide the wavelengths specifically required by the certain plants. Plants will be able to grow and flourish more splendidly with ALTLED grow lights.
Q : How do you calculate ALT LED lifespan?
A :LED MR16、LED燈管、LED燈泡較省電,壽命較傳統燈長,不需經常更換,且LED燈不含汞及有害物質,更加環保,不破壞環境。
Q: How do you calculate electricity bills?
A: Daily electricity usage(Hrs) x Watts(W)÷1000(W) = Power consumption per day
Q: What is IP68?
The protection classification offered by an enclosure is shown by the letter IP (Ingress Protection) and two digits.
The first digit indicates solid particle protection.
The second digit indicates the protection against water.
First digit: 6
Second digit: 8
Q:What is PF(POWER FACTOR)? Which ALTLED products provide high PF (HPF)?
A:The power factor of an AC electrical power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load, to the apparent power in the circuit and is a dimensionless number between -1 and 1.
The higher the power factor, the better for energy-saving. For example, if the lamp’s power factor is 0.5, the power plant must supply more power to the lamp compared with a lamp which has 0.9 power factor; Although the cost difference will not directly be charged to the user, the extra energy is wasted and therefore not efficient nor environmental friendly.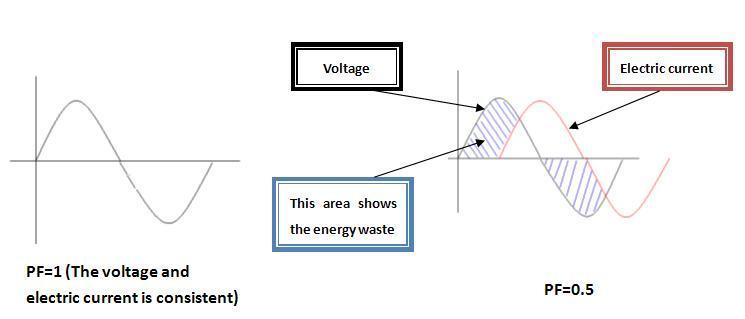
ALTLED with high PF ( ≥ 0.9) :
LED MR16, LED A55 bulb, LED T8 tube, LED PAR30, LED PAR38, LED BR40, LED Grow light, LED anti-explosive lamp, LED Street light, LED Floodlight…etc.
Q: What is the advantage of ALT’s heat dissipation technology?
A:Heat dissipation is very important to LED lamps.
The heat will cause the damage of LED chip, which is associated with the lifespan of the lamp, is usually affected by the heat generated within the lamp. Affiliated with the fourth largest server supplier in the world, ALT is the first LED lighting company to transfer the technological know-hows of the server industry to LED lighting. ALT developed an excellent aluminum heat fin design and obtained several international certification and patents. ALT’s MR16 has the largest cooling area. (ALT MR16’s cooling area is 25,000 mm ², while Philixx: mastxx’s cooling area is only 4,000 mm ²) C compared with to other brands in the led LED market, . ALT’s products pay a lot of effort on lamp’s heat dissipation technology, so the lamps have higher stability and longer lifeoffer the best heat dissipation in the industry, and therefore guaranteeing best quality and longest lifespan.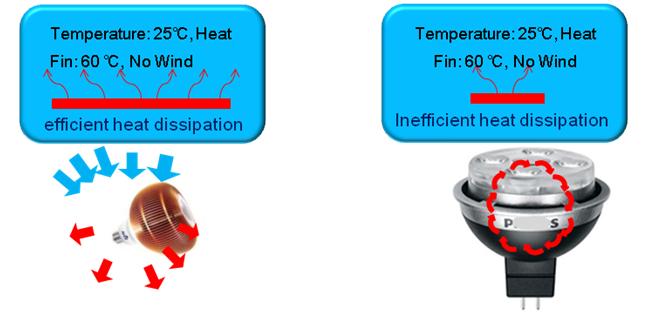
Q:Global phase-out schedule of incandescent light bulbs?
Australia:Disallow most sales of Ban the production of incandescent light bulbs by 2009 and ban the use of incandescent light bulbs by 2010.
European Union:All member states of the EU agreed to a progressive phase-out of incandescent light bulbs by 2012.
Canada:On 31 December 2014 the import of 40- and 60-watt bulbs will be banned.
Taiwan:Taiwan banned production and, imports of incandescent lighting starting from 2012.
USA:America started to phase out traditional 100-watt incandescent light on Jan. 1, 2012.
Japan:Japan banned production and, imports of incandescent lighting starting from 2012.
Korea:Korea banned production, and imports of incandescent lighting starting from 2014.
China:China banned imports and sales of certain incandescent light bulbs started starting from October 2012.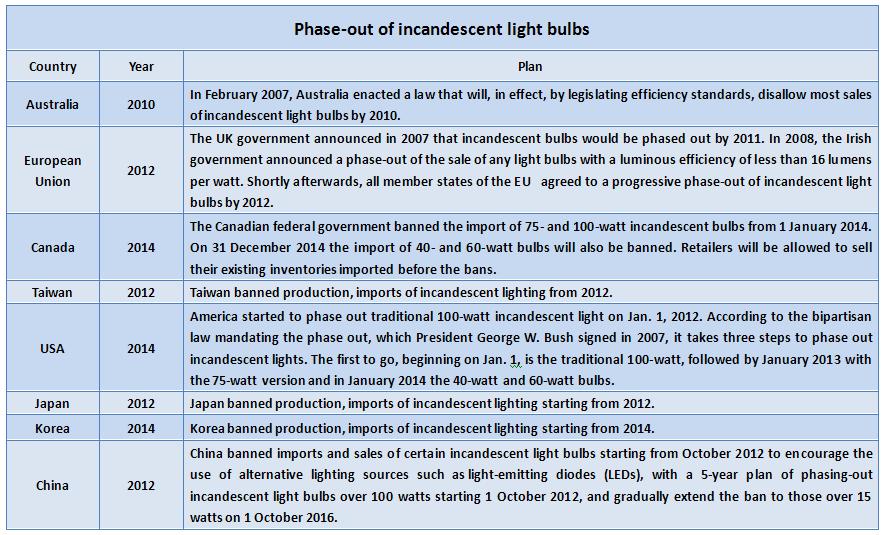
LED (Light-Emitting Diode)
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for general lighting. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, early LEDs emitted low-intensity red light, but modern versions are available across the visible, ultraviolet, and infrared wavelengths, with very high brightness. When a light-emitting diode is switched on, electrons are able to recombine with holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence, and the color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy band gap of the semiconductor. An LED is often small in area (less than 1 mm2), and integrated optical components may be used to shape its radiation pattern. LEDs have many advantages over incandescent light sources including lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, improved physical robustness, smaller size, and faster switching. However, LEDs powerful enough for room lighting are relatively expensive, and require more precise current and heat management than compact fluorescent lamp sources of comparable output. Light-emitting diodes are used in applications as diverse as aviation lighting, automotive lighting, advertising, general lighting, and traffic signals.
LED Glossary: Illuminance
Illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of the intensity of the incident light, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception. Similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per unit area emitted from a surface. Luminous emittance is also known as luminous exitance.
CRI (Color Rendering Index)
It is a measure of the degree of color shift objects undergo when illuminated by the light source as compared with those same objects when illuminated by a reference source of comparable color temperature.
Beam angle
It is referred to the angle between the two directions for which the intensity (candlepower) is 50% of the maximum intensity as measured in a plane through the nominal beam centerline (center beam candlepower).
Luminous flux
Luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of light emitted, in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light.
Luminous efficacy - unit : lm/W
Luminous efficacy is a property of light sources, which indicates what portion of the emitted electromagnetic radiation is usable for human vision. It is the ratio of emitted luminous flux to radiant flux. Luminous efficacy is related to the overall efficiency of a light source for illumination, but the overall lighting efficiency also depends on how much of the input energy is converted into electromagnetic waves (whether visible or not).
LED Glossary: Luminous intensity
Luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye.
Heat sink
It is a part of the thermal system that conducts or convects heat away from sensitive components, such as LEDs and electronics.
Color temperature - unit : K
Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, and other fields. The color temperature of a light source is determined by comparing its chromaticity with that of an ideal black-body radiator. The temperature (usually measured in kelvin (K)) at which the heated black-body radiator matches the color of the light source is that source's color temperature; for a black body source, it is directly related to Planck's law and Wien's displacement law. Counterintuitively, higher Kelvin temperatures (5000 K or more) are "cool" (green–blue) colors, and lower color temperatures (2700–3000 K) "warm" (yellow–red) colors. Cool-colored light is considered better for visual tasks. Warm-colored light is preferred for living spaces because it is considered more flattering to skin tones and clothing. Color temperatures in the 2700–3600 K range are recommended for most general indoor and task lighting.
Lifespan – LED luminaries
It is determined by the actual usable life of the many components included in the lighting system and the manufacturer’s expected lumen maintenance. Each of the components must be analyzed independently in order to provide an accurate assessment, because the lamp/luminaire’s lifespan will be as long as the shortest lifespan of any of its components (like power supply/driver units).


